Description
Views: 79
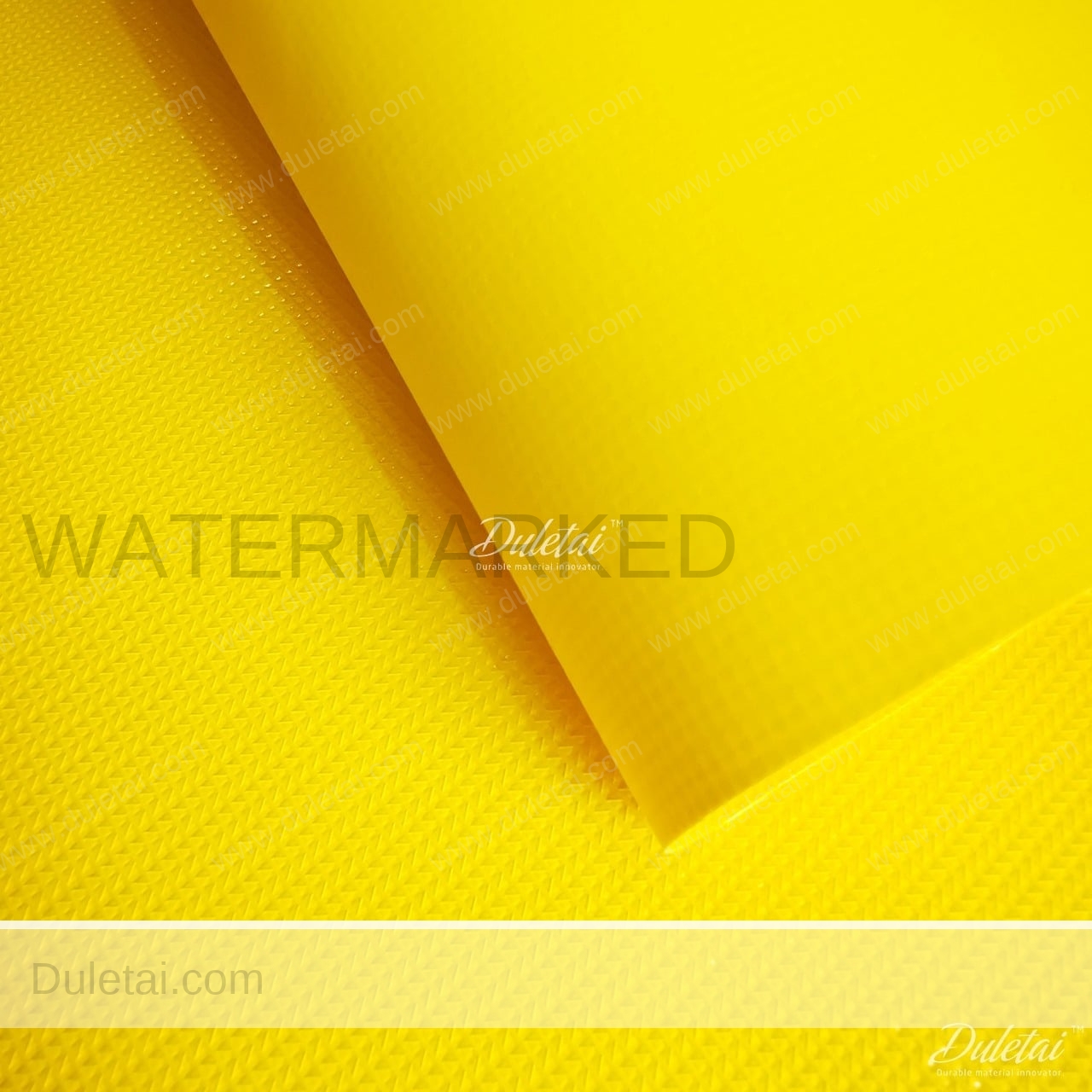
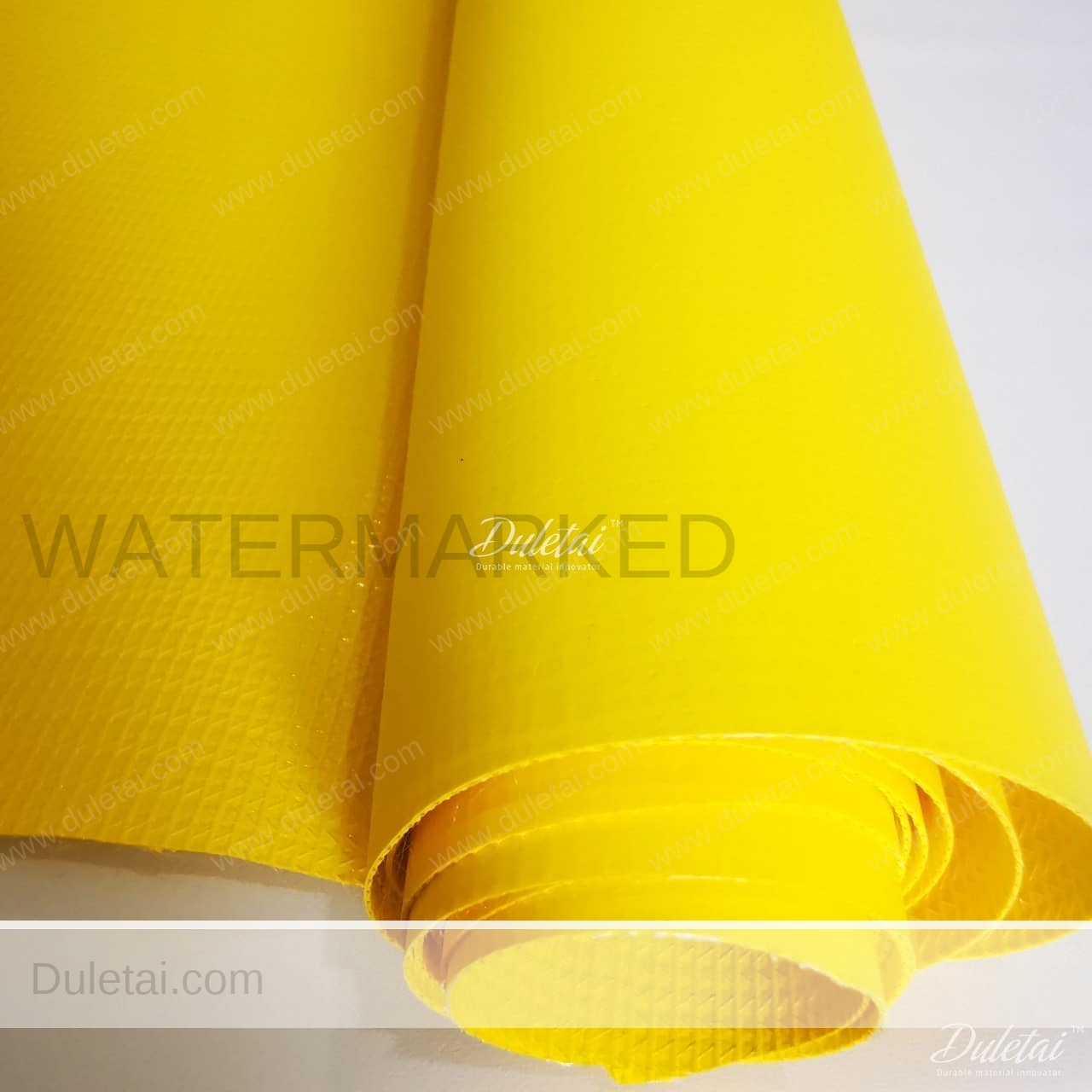
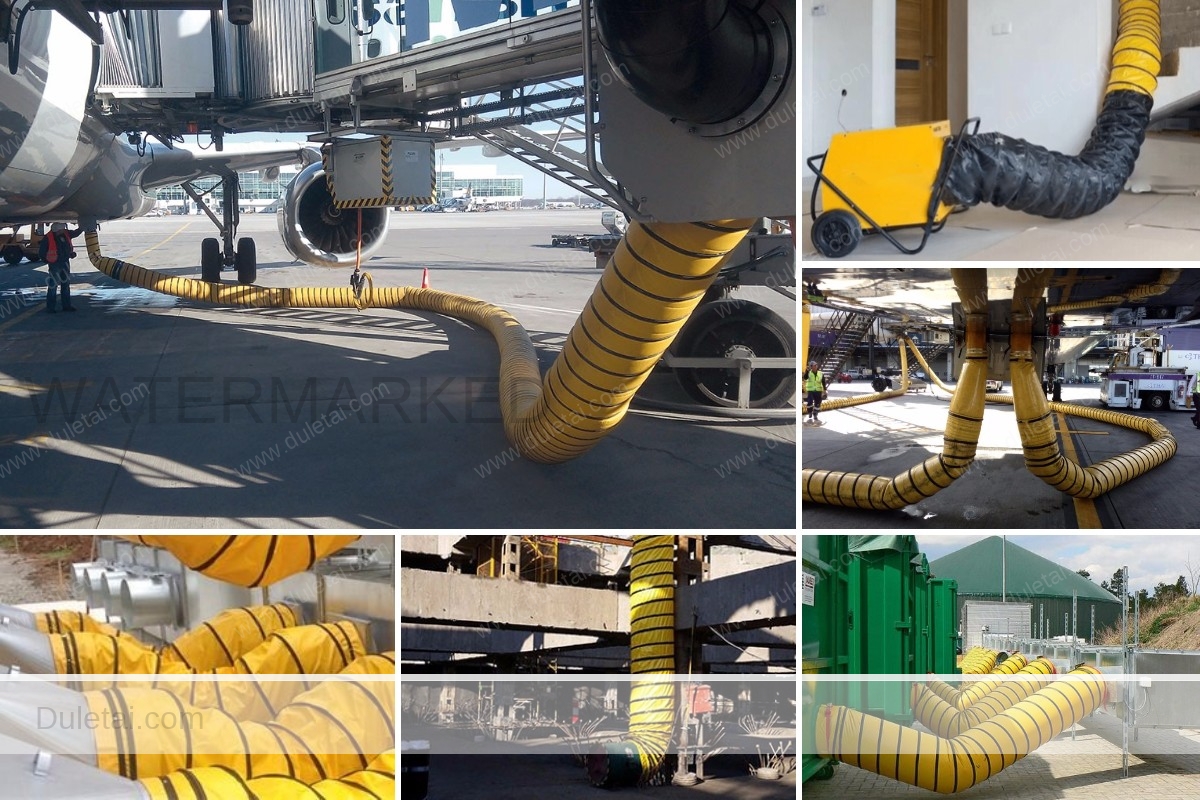
Air duct material is an innovative and cost effective fabric alternative to traditional metal ductwork providing precise and efficient heating, cooling, or ventilating for virtually any building application. This PVC fabric comprises of a woven high tenacity polyester base fabric and a flexible plasticised PVC coating (applied to both sides of the polyester base fabric) is completely waterproof, fire retardent, anti-static,very strong and durable. Suitable for for duct application, fire water mains, gas pipeline, gymnasiums, pools, food processing, fitness centers, convention centers, schools and warehouses.

Air duct material specifications:
| Ventilation duct material | DuraTarps DLT-5304 | |
| Structure: | 3-Layer: PVC+Polyester+PVC |
| Base fabric: | 1000D |
| Width: | 1.02m-3.2m |
| Weight: | 600g(±10g)/sqm |
| Colour: | RAL1018 |
| Flame retardant: | FR DIN4102 B1, M2, CLASS 1 |
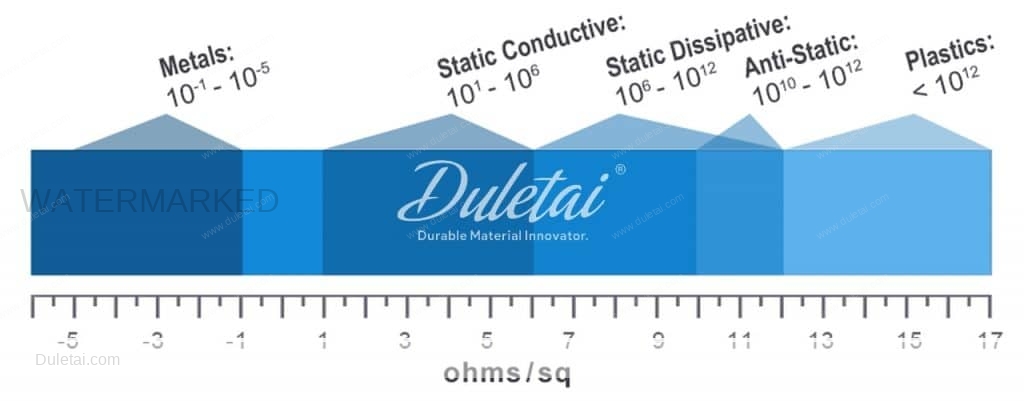
| Anti-static: | 108 (Ω) |
| Suitable temperature: | -20° to +70° |
| Package: | Paper tube + Craft paper |
| Meter per roll: | 30m-506m |

Air duct material features:
- Matt/Glossy finish0
- Strong and durable
- Wipe clean
- Completely waterproof
- Suitable for all weather conditions
- Can be sewn or high frequency welded
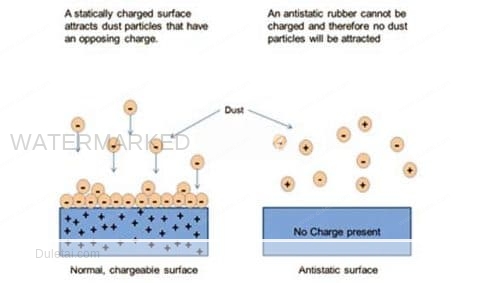
About Anti-Static
- Static Electricity
- As the name implies, static electricity is electricity at rest. The electrical charge is the transference of electrons that occurs when there is sliding, rubbing, or separating of a material, which is a generator of electrostatic voltages. For example: plastics, fiber glass, rubber, textiles, ect. Under the right conditions, this induced charge can reach 30,000 to 40,000 volts.
When this happens to an insulating material, like plastic, the charge tends to remain in the localized area of contact. This electrostatic voltage may then discharge via an arc or spark when the plastic material comes in contact with a body at a sufficiently different potential, such as a person or microcircuit.
If Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) occurs to a person, the results may range anywhere from a mild to a painful shock. Extreme cases of ESD, or Arc Flash, can even result in loss of life. These types of sparks are especially dangerous in environments that may contain flammable liquids, solids or gasses, such as a hospital operating room or explosive device assembly.
Some micro-electronic parts can be destroyed or damaged by ESD as low as 20 volts. Since people are prime causes of ESD, they often cause damage to sensitive electronic parts, especially during manufacturing and assembly. The consequences of discharge through an electrical component sensitive to ESD can range from erroneous readings to permanent damage resulting in excessive equipment downtime and costly repair or total part replacement.
How is static resistance measured?
Static resistance is measured in Ohms (Ω) and can be measured using what are called Ohm meters (a common instrument in most workshops). Resistance measurements will fall somewhere between 0 (for a truly conductive material such as metal or water) and infinity (for truly insulative materials such as rubber and fabrics). Resistance measurements for plastic materials with some level of conductivity are usually measured in Mega-Ohms (MΩ). 1 Mega-Ohm = 1,000,000 (1 million) Ohms.
- Anti-Static
- Preventing the buildup of static electricity. Reducing static electric charges, as on textiles, waxes, polishes, etc., by retaining enough moisture to provide electrical conduction.